The first symptoms to look out for
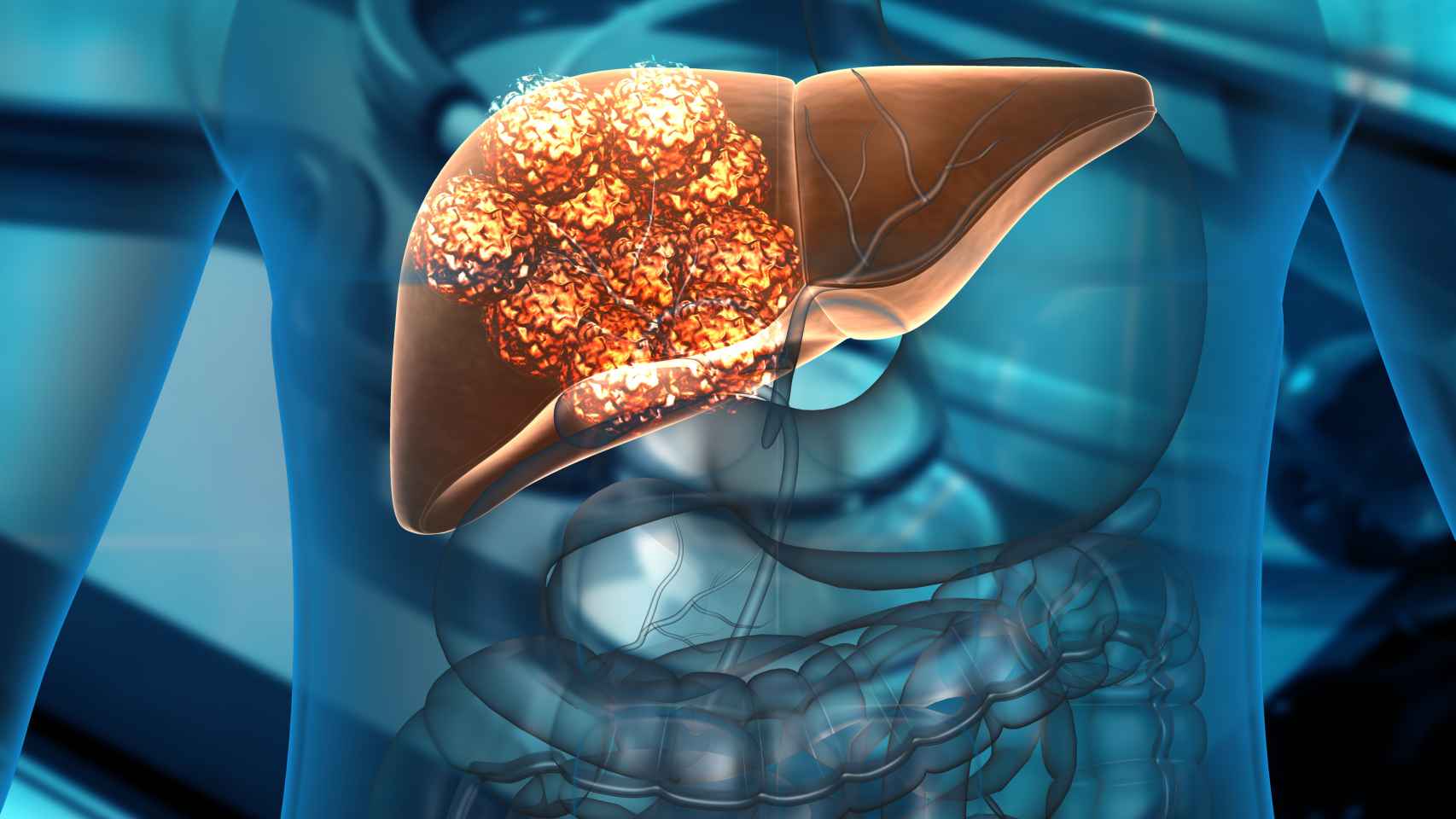
Liver cancer has established itself as one of the leading causes of death worldwide, ranking third cause of death from cancer. It is also the sixth most commonly diagnosed disease in the world, although it primarily affects men in most countries, with morbidity and mortality rates 2–3 times higher than in women in most countries. An estimated 87,000 people were diagnosed with liver cancer in Europe in 2020.
The situation in Spain is no less alarming. On the contrary, according to a report on cancer rates in Spain, In 2021, 5,066 people died from malignant liver tumors. and intrahepatic bile ducts, and an estimated incidence of 6,695 new cases of liver cancer in 2023.
Pay attention to symptoms
Spanish Society of Medical Oncology (SEOM) warns that Symptoms of liver cancer usually appear in advanced stages.when the disease has progressed significantly. In many cases, patients may remain asymptomatic until the cancer is very advanced and the signs that appear are not unique to that disease.

One of the most common warning signs is unexplained weight loss, as well as persistent loss of appetite. This lack of appetite is usually accompanied by severe fatigue or weakness, which significantly affects the energy and general condition of the patient.
TO abdominal levelSigns such as enlargement or bulging in the upper right side of the abdomen may appear, accompanied by persistent pain in the upper central area. The patient also often experiences progressive abdominal bloating. Another important symptom is jaundice, which is a yellowish-greenish discoloration of the skin and eyes due to problems with liver function.
In this digestive zoneAfter eating a small amount of food, nausea, vomiting and early satiety may occur, further affecting the patient’s nutritional status. Changes in the color of urine and stool may also occur: dark urine (choluria) and pale or whitish stools (acolia).
Other symptoms include severe generalized itching of the skin, as well as confusion or excessive sleepiness, especially in the later stages of the disease. Additionally, in people with a history of cirrhosis or chronic hepatitis, worsening general condition may indicate progression to hepatocellular carcinoma, the most common type of liver cancer.
Causes and prevention of liver cancer
Liver cancer is a disease characterized uncontrolled growth of liver cells that can invade healthy tissue and spread to other parts of the body (metastasis). This cancer may be primary (starting in the liver) or secondary (metastatic when other tumors spread to the liver). In addition, there are benign liver tumors that, although not cancerous, require monitoring.
According to the Spanish Association Against Cancer (AECC), this a complex disease, the causes of which are not fully understood. However, there are risk factors well identified. Among the most significant are cirrhosis of the liver, which affects 50% to 80% of patients with liver cancer; chronic infections of hepatitis C and B; and exposure to toxic substances that can damage the liver over time.
Additionally, a combination of certain lifestyle factors such as tobacco use, alcohol and obesitysignificantly increases the risk of liver cancer, which is more common in men, possibly due to greater exposure to these habits.
Given the fundamental role of these factors, prevention liver cancer is based on reduce exposure and in identifies people at high risk for more thorough preventive monitoring. The AECC highlights some key recommendations:
– Prevention of hepatitis B and C. Vaccination against hepatitis B virus (HBV) and access to effective antiviral treatment for hepatitis B and C are important measures to reduce the incidence of liver cancer, given that there is no vaccine for hepatitis C virus and its prevention depends on preventing initial infection and effective antiviral treatment.
– healthy lifestyle. Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, maintaining an adequate weight, and quitting smoking are important practices for reducing the risk of liver cancer. Obesity increases the risk of fatty liver disease and diabetes, both conditions associated with an increased risk of liver cancer.
– Toxic Exposure Control. Reducing your exposure to certain chemicals, such as some compounds found in tobacco smoke and some industrial processes, is key to preventing liver cancer.
