A shocking study from the Pasteur Institute reveals the little-known effects of tobacco on our immune system.
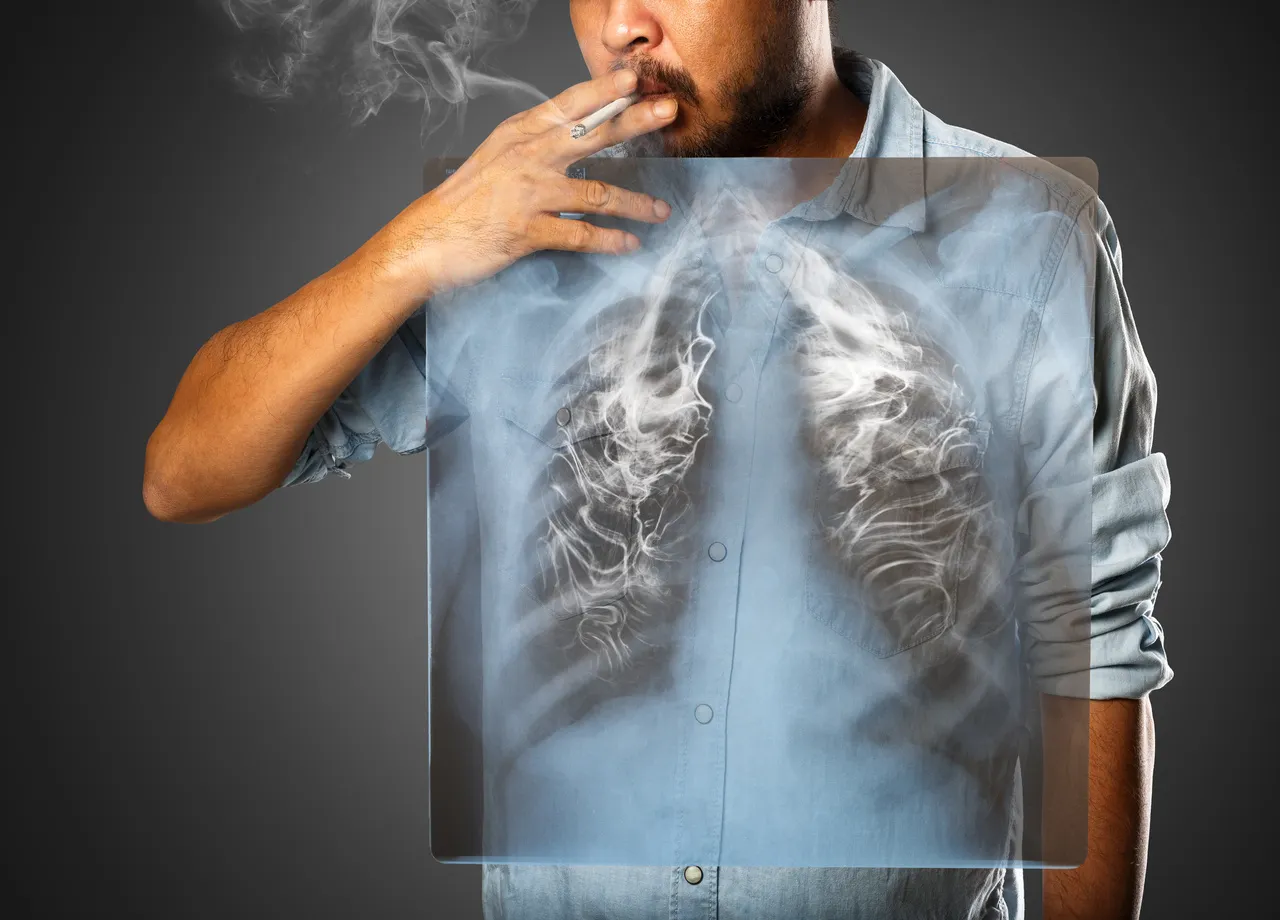

For the first time, a landmark study highlights the harmful and long-term effects of smoking on the immune system.
This study carried out by the Pasteur Institute shows that The profound changes that smoking causes in the body’s ability to defend against microbial attacks. Although smokers appear to bear the stigma of their toxic habit, researchers are uncovering the mechanisms underlying this immune transformation.
In this unprecedented study, Darragh Duffy, head of the Department of Translational Immunology at the Institut Pasteur, reveals the hidden side of the insidious immune disorder that It affects both the inflammatory response and the adaptive mechanisms of the defense system.
Thanks to a thorough analysis of the immune systems of more than 1000 people, This studiopublished in a prestigious magazine Nature, sheds light on a new chapter in understanding the destructive effects of tobacco In health.
Smoking, BMI and cytomegalovirus
The study focused on intercellular communication through cytokines. proteins secreted by immune cells assess the quality of the immune response.
Smoking alters adaptive immunity with lasting effects
The role of smoking in the short- and long-term regulation of immune responses. https://t.co/7qL6L9uAYk pic.twitter.com/aHvIAWeia6
— AgingdocDavid BarzilaiMD PhD, MS, MBA, DipABLM (@agingdoc1) February 16, 2024
Blood samples from participants in the Indoor Environment group were exposed to a variety of microorganisms. which revealed diverse and complex immune responses.
Changes in the mechanisms of adaptive immunity persist for decades.
Among the key factors that distinguish people with an impaired immune response are: Smoking, body mass index (BMI), and latent cytomegalovirus infection have important influences. along with age, gender and genetic factors.
Stronger inflammatory response
Researchers have identified two important abnormalities in smokers: exacerbation of the inflammatory response during infection and changes in the activity of cells involved in immune memory.
This discovery highlights the harmful effects of tobacco on the innate and adaptive defense mechanisms of the immune system, thereby increasing the risk of infectious complications and chronic inflammation in smokers.
Persistence of effects after quitting smoking
Although the inflammatory response appears to normalize quickly after smoking cessation, Changes in the mechanisms of adaptive immunity persist for decades. This discovery highlights the immune system’s memory, which retains the effects of smoking even after giving up this bad habit.
What implications does this have for immune memory?
Similarities found between immune profiles of current and former smokers have raised questions about the mechanisms underlying this persistent immune memory..
Smoking alters adaptive immunity with lasting effects@Nature Will other impacts have similar consequences, and then what? Would alcohol have a similar effect? https://t.co/trFeaCr1IY pic.twitter.com/bhScidwLXi
— Xiaotao Jiang (@Titus12629950) February 15, 2024
Researchers have identified epigenetic modifications to DNA that They alter the expression of genes involved in immune cell metabolism.
This discovery opens up new perspectives To better understand the effects of smoking on immunity, both in healthy individuals and in those who suffer from various pathologies.
By identifying the profound changes caused by smoking in the immune system, This study highlights the critical importance of smoking prevention and cessation for maintaining health.
In addition to the known cardiovascular and pulmonary risks, Smoking also leaves a lasting mark on the body’s ability to defend itself. infectious and inflammatory diseases.
Link to news:
Saint-André V., Charby B., Beaton A. and others. Smoking alters adaptive immunity with lasting effects. Nature 626, 827–835 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06968-8
