macromolecule that honors pokemon
Who doesn’t know the famous franchise Pokemon? Developed by Game Freak and published by Nintendo and The Pokémon Company, the series has already become part of pop culture and, like many of its main characters, present in various ways in modern society. In fact, in 2008, the franchise even went beyond science and also made its way into in the world of molecular biology: A team of researchers from Osaka University in Japan decided to use the name of one of the main characters, Pikachu, for the name of a newly discovered protein. Thus was born Pikachurin protein.
This connection not only bears the name of one of the most recognizable symbols in fiction, but also plays a crucial role in the structure that allows our eyes to convert light into images that the brain can understand. Their discovery has since opened the door to a much greater understanding of how the fine structure of the retina is formed and maintained, and has laid the foundation for new medical avenues to combat vision disorders.
SYNAPSES OF CELLS
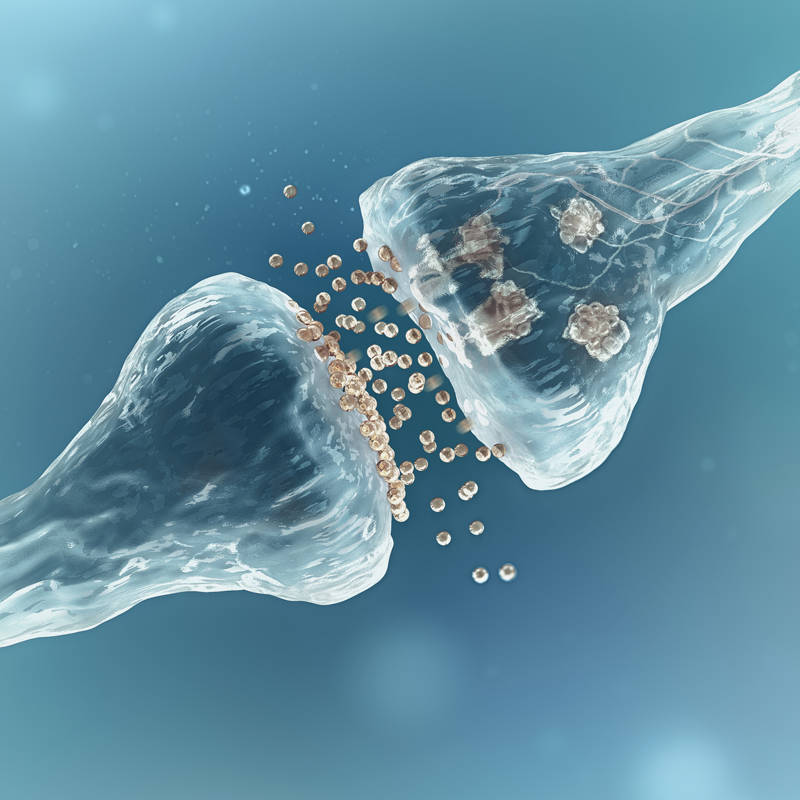
But what exactly is the role of this protein? So, Pikachurin is located precisely in the synaptic cleft of photoreceptor cells. To understand this we must take into account that synapse this is the process that allows neurons communicate with each other and with other cells. This is an action that occurs through nerve impulses that are transmitted to the neighboring cell through certain substances called neurotransmitters.
Thus, it seems clear that for the central nervous system to function properly, this synapse must be absolutely accurate and did not provide any solution. Thanks to this, we can move our joints, move around, perceive smells, touches, images… In particular, right in the retina of the eye there is a type of cell called photoreceptors which transmit information to other cells at a specialized synapse called ribbon synapses. Well: Researchers have determined that our retinal protein Pikachurin It operated right at the center of this special synapse.
In fact, the same researchers studied mice that had mutations that completely abolished the expression of this protein, resulting in its absence. While observing the results, they found that the tips of the photoreceptor cells they didn’t quite fit with those of the remaining cells, causing irregular and imprecise synapse and, therefore, very serious changes in signal transmission and visual function.
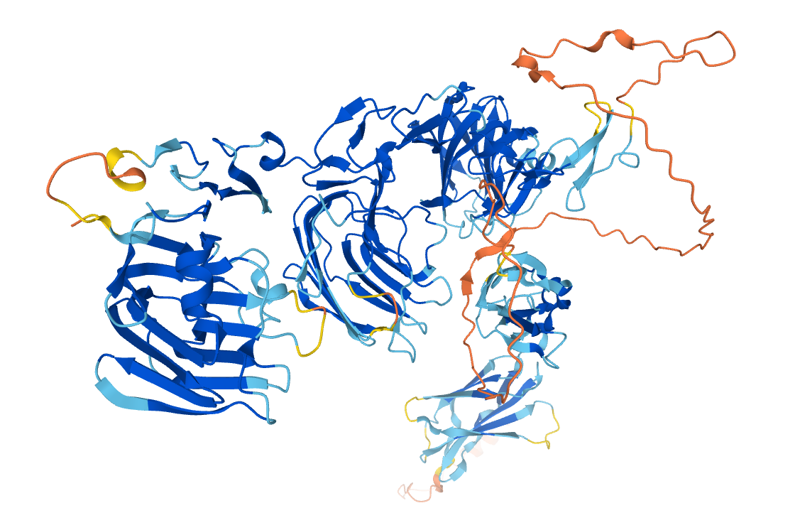

protein structure Pikachurin.
PIKACHURRINA: THE FUNDAMENTAL ELEMENT
In addition, the researchers found that the Pikachurin protein colocalizes with two other proteins in these synaptic processes: dystrophin and dystroglycan, indicating that it plays a key role in the organization and stability of this structure. As if that weren’t enough, the fact that it interacts biochemically with these two proteins suggests that they all work together and maintain harmony integrity and functionality ribbon synapse and, therefore, allow the brain to correctly interpret the signals detected by the photoreceptor cells of the eyes.
The biggest implication of this discovery is its importance when it comes to understand anomalies which arise in the retinas of patients with muscular dystrophy, a genetic disease that affects muscles but can also have side effects in other tissues, including the retina. Thus, by understanding how Pikachurin and its interactions promote proper synapse production, researchers will be able to see the mechanisms underlying the visual changes associated with this disorder.