Sexually transmitted diseases are on the rise
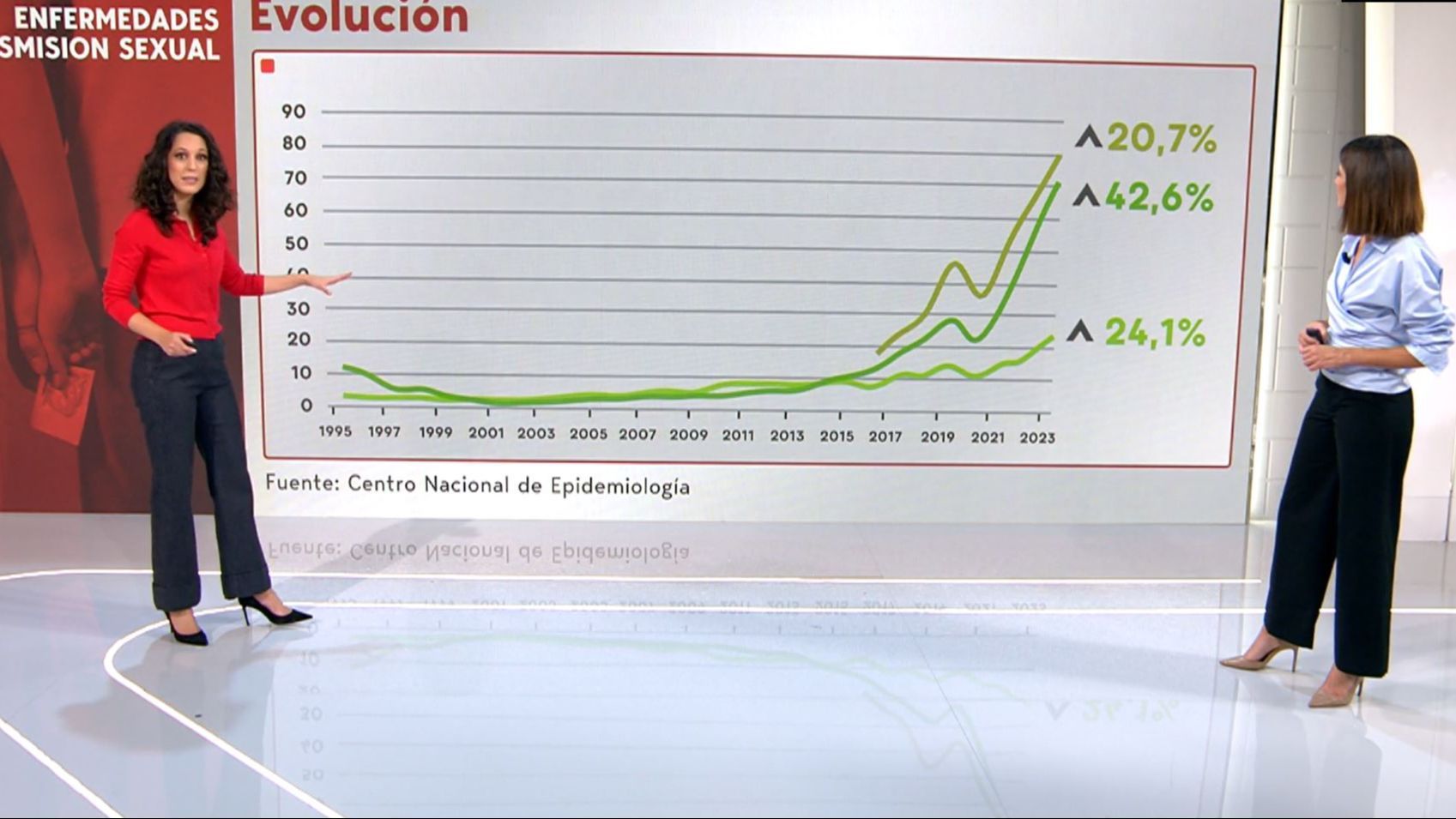
sexually transmitted diseases are shotespecially, gonorrhea which grew by more than 42% in just two years. This disease, manifested by a burning sensation when urinating and discharge, has spread the most, but it is not the only thing that worries us. men from 20 to 34 years old This is the most common profile of diseases that are treated with antibiotics and prevented with condoms.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) continue to spread. Growth trend in Spain over the past yearwith an increase of 42.6 percent for gonococcal infections, or gonorrhea, and 24.1 percent for syphilis between 2021 and 2023, as shown in the report “Epidemiological Surveillance of Sexually Transmitted Infections in Spain 2023” published by National Epidemiology. Specifically, the report states that there were 34,403 cases of gonococcal infections reported in 2023, compared to 16,115 in 2021 or 25,449 in 2022. For syphilis, there were 10,879 cases reported in 2023 for comparison. up to 6841 in 2021 and 8531 in 2022. Likewise, the increase in chlamydia incidence was 20.7 percent annually between 2016 (the first year for which data is available, with 7,239 cases) to 2023 (36,983 cases).
Morbidity gonococcal infection in autonomous communities In 2023, it is represented in a very wide range: from 9.24 to 165.30 cases per 100,000 inhabitants. The highest rates were recorded in Catalonia (165.30), Madrid (94.08), Basque Country (78.37) and Andalusia (58.64). The lowest rates were recorded in Ceuta (1.20), Melilla (2.34), Aragon (9.24), Castile and Leon (12.59) and Extremadura (16.12).
Of the total reported cases, 44.2 percent (15,216 cases) had transmission information. Of these, 39.3 percent corresponded to homosexual relationships between men, 5.8 percent to men with heterosexual relationships, 17.2 percent to heterosexual relationships among women, 34.5 percent to men with unspecified sexual transmission and 3.2 percent to women with unspecified sexual intercourse. in eight cases diagnosed in newborns transmission occurred from mother to child.
Regarding cases of syphilisThe autonomous communities that reported the highest rates in 2023 were the Canary Islands (53.91), the Balearic Islands (33.97), Madrid (32.52) and Catalonia (30.54). The lowest incidence was in La Rioja (2.17), Castile-La Mancha (3.36) and Aragon (6.11).
As with gonococcal infection, rates were higher in men (40.66) than women (5.27), and the age group with the highest rates was 25 to 34 years (64.97 per 100,000).
The report included seven confirmed cases of early congenital syphilis.
The report also includes seven confirmed cases of early congenital syphilis (under two years of age) in 2023. The diseases corresponded to five boys and two girls, all of whom were diagnosed in the first months of life.
Regarding Chlamydua trachomatis infection, rates increased between 2016 and 2023 in autonomous communities around the world reporting cases. In 2023 the highest rates were observed in Catalonia (194.56), Navarre (124.97), Basque Country (102.78) and Madrid (85.97). Those with lower scores were Melilla (1.17), Aragon (5.52), Castile and Leon (13.26) and Castilla-La Mancha (13.82). Ceuta reported no cases.
46.6 percent (17,238 cases) were women, and the average age at diagnosis was 28 years, with women being younger than men (24 years and 31 years, respectively). most cases happened between 25-34 years (36.4 percent) and 20-24 years old (25.6 percent). The percentage of cases between the ages of 15 and 19 was 9.9 percent, with 16.2 percent of the total cases occurring in women and 4.4 percent in men.
Finally, regarding lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV), an infection caused by Chlamydia trachomatis L1-L3, the report states that 1,807 cases were reported in 16 autonomous communities that have a surveillance system. The highest rates were observed in Catalonia, the Community of Madrid, Navarre and the Basque Country. The CCAA of Cantabria, Castile-La Mancha, Ceuta and Melilla did not declare any cases of the disease in 2023.
Difficulty in comparing incidence rates between autonomous communities.
On the other hand, the report warns of the difficulty of comparing incidence rates between autonomous communities due to differences in their surveillance systems. Although all communities have individual case reports, please call. improve data quality, especially regarding the method of transmission.
To combat the growing problem of STIs, Spain has launched Infection Prevention and Control Plan HIV and STIs 2021–2030, with the goal of eliminating these infections as a public health problem by 2030. The plan is based on a comprehensive approach that includes prevention, early diagnosis, treatment, chronic disease care and improving quality of life, while not forgetting the fight against stigma and discrimination.
