The Euclid mission reveals millions of stars and galaxies in the first part of a large map of the Universe.

The European Space Agency (ESA) Euclid space mission presented the first fragment of his future great map of the Universea huge mosaic of fourteen million galaxies, that’s only 1% of what the telescope is going to show us in the coming years.
Mosaic size 208 megapixels. contains 260 observations of Euclid held from March 25 to April 8 this year. In just two weeks, the telescope covered 132 square degrees of the southern sky (more than 500 times the area of the full Moon) in exquisite detail.
The fragment was discovered at the International Astronautical Congress in Milan, Italy, by ESA Director General Josef Aschbacher and Scientific Director Carol Mundell.
Launched in July 2023, Euclid It began planned scientific observations on February 14, 2024. In November 2023 and May 2024, he showed the world his first images of stunning quality.
Euclid will pass We’ve been scanning the sky for six years and observing the shapes, distances and movements of billions of galaxies up to 10 billion light years away.
Given all this information, Euclid will perform largest 3D space map ever createdwhich will expand our knowledge of the hidden influence of dark matter, the expansion of the Universe and gravity.
Currently this first fragment contains tens of millions of stars in our galaxyThe Milky Way and fourteen million galaxies.
“This stunning image is the first part of a map that will show more than a third of the sky in six years. This is only 1% of the map, and yet it is filled with a huge variety of sources that will help scientists discover new ways of describing the Universe,” said Valeria Pettorino, Euclid Project Scientist at ESA.
Unprecedented detail
The spacecraft’s sensitive cameras captured an incredible number of objects in exquisite detail.
By zooming in on the mosaic (this image is 600 times larger than the full view), the complex structure can be clearly seen. spiral galaxy structure.
A special feature of the mosaic is the faint clouds between the stars of our galaxy. appear in blue on a black background of spaceare a mixture of gas and dust that are also called “galactic cirrus clouds” because they look like cirrus clouds.
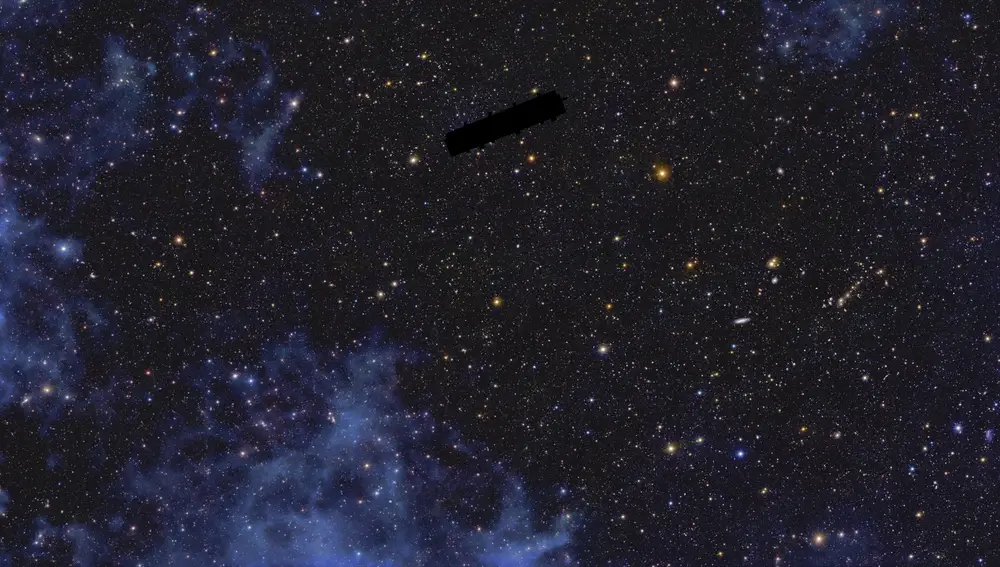

Euclid can see these clouds with his ultra-sensitive visible light camera because they reflect the optical light of the Milky Way.
Clouds too they glow in the far infrared rangeas observed by ESA’s Planck mission.
The mosaic released is just a preview of what the Euclid mission will bring us since it began its routine science observations last February. completed 12% of the study.
53 square degrees of review have been published, including a preview of Euclid’s deep field regions. scheduled for March 2025 and the mission’s first year of cosmological data will be available to the community in 2026.