a new and unique window for analyzing the Universe
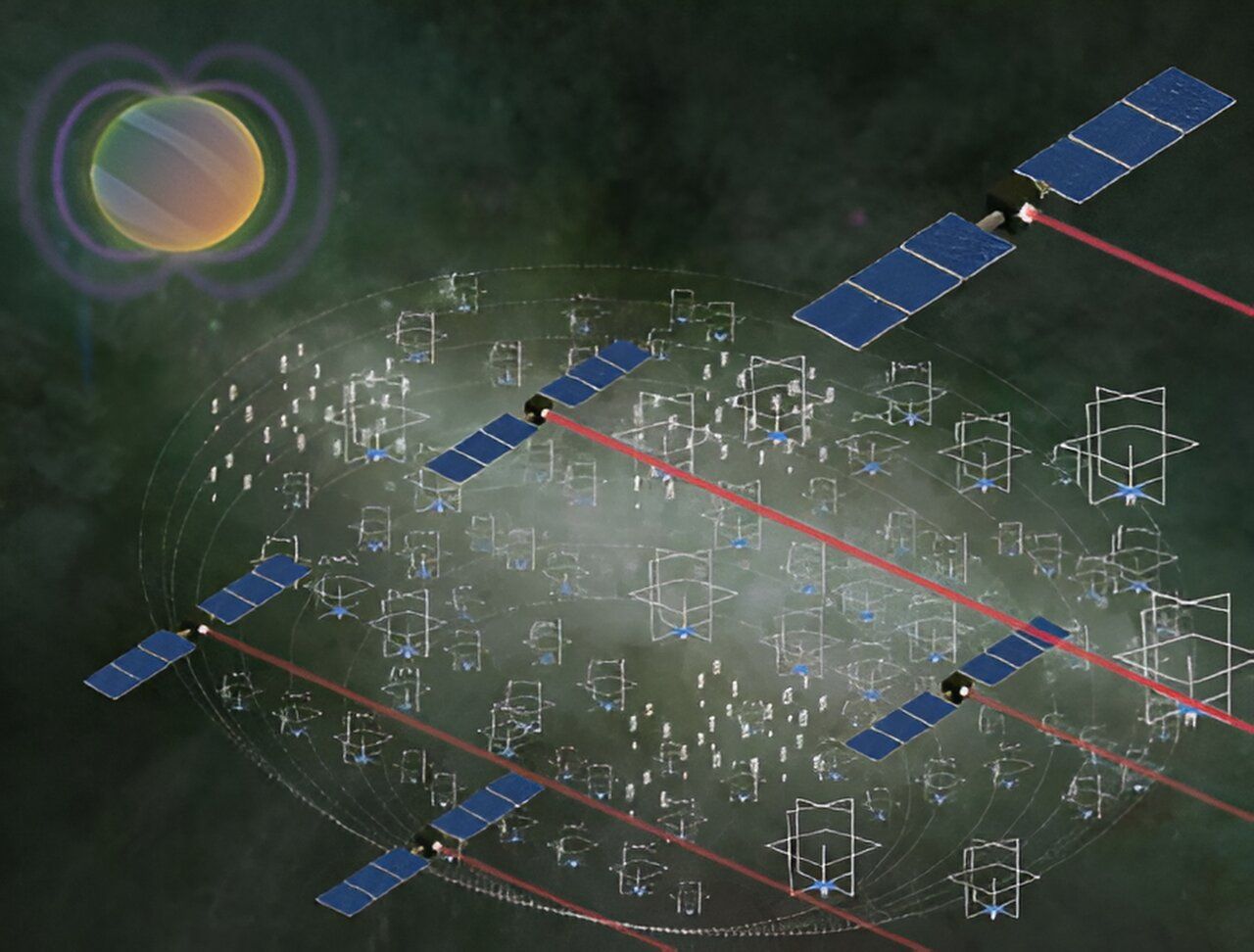
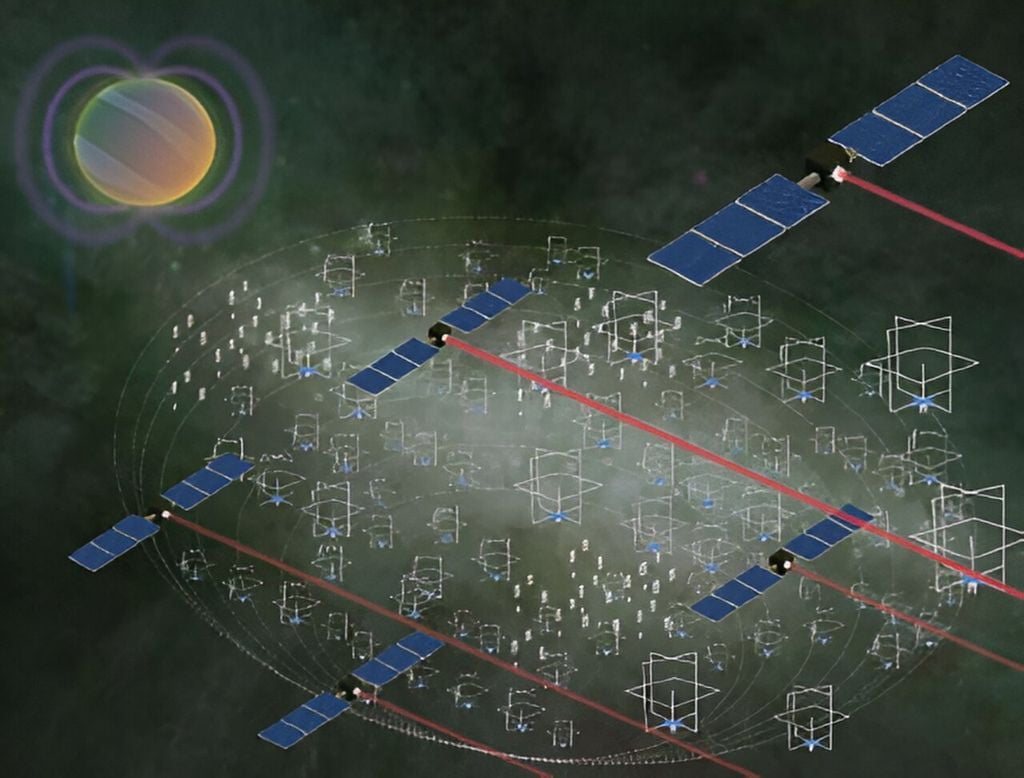
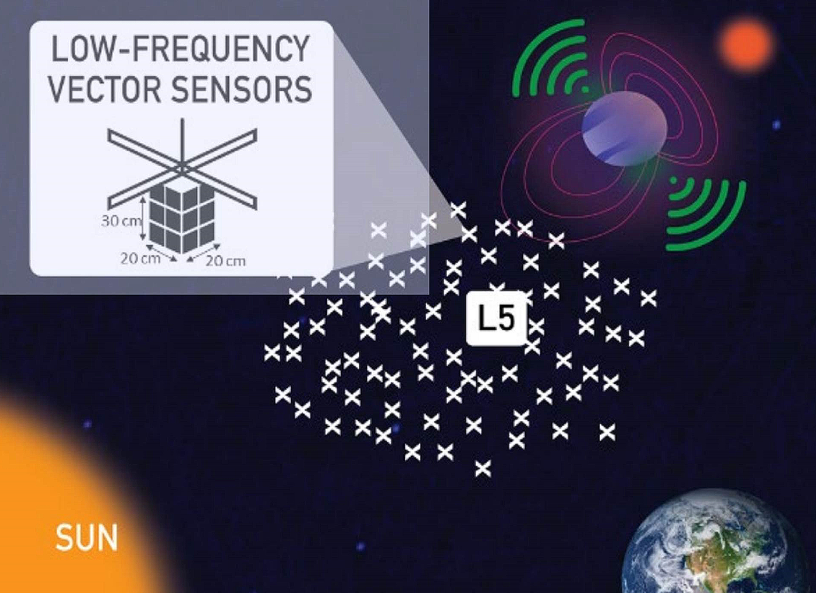
low frequency electromagnetic radiation contains important information about exoplanetary and stellar magnetic fields (a key ingredient for habitability), the interstellar/intergalactic medium, and the first stars and galaxies.
On the way to the Large Longwave Observatory
According to POTHe Large Longwave Observatory (Large Long Wave Observatory, GO-LoW) offers interferometric array of thousands of identical small satellites at the Earth-Sun Lagrange point (for example L5) for measure the magnetic fields of exoplanets terrestrial creatures by detecting their radio emissions at frequencies from 100 kHz to 15 MHz. Each spacecraft will be equipped with an innovative vector sensor antenna that will enable the study of exoplanet magnetic fields at 5 parsecs for the first time.
Moving away from the traditional approach of relying on one large and expensive spacecraft (i.e. HST, Chandra, JWST) with many individual points of failure, A large interferometric observatory consisting of thousands of small, cheap and easily replaceable units..
Interferometrytechnology that combines signals from many spatially separated receivers into a large “virtual” telescope.ideal for astronomy long waves. Individual antenna-receiver systems are simple, do not require large structures, and the large distance between nodes provides high spatial resolution.
In a NASA study Phase Iit was discovered that the hybrid architecture of the constellation turned out to be the most effective. Small, simple listening nodes (LNs) collect raw radio data using a deployable vector sensor antenna. A small number of larger and more capable “communications and compute” nodes (CCNs) collect LN data over a local radio network, perform beamforming processing to reduce the data volume, and then transmit the data to Earth via free space optics.
Cross-correlation of beamforming data is performed on Earth. where computing resources are not strictly limited. CCNs are also responsible for constellation management, including timing and scale. The Phase I study also found that the LN-CCN architecture optimizes packaging efficiency by allowing a small number of super-heavy launch vehicles (such as Starship) to deploy an entire constellation on L4.
The Phase I study showed that the key innovation for GO-LoW He “system of systems“.The technologies required for each individual part of the observatory (e.g., laser communications, CubeSats, distance measurement, timing, data communications, data processing, orbital propagation) are not a huge leap from the current state of the art. , but coordination Creating all these physical elements, data products and communication systems is new and complex, especially at scale.
The proposed study will address the following questions:
– Develop a real-time, multi-agent simulation of a GO-LoW constellation. demonstration of the autonomous operations architecture required to create a large constellation (up to 100 thousand) beyond Earth orbit.
– Continue to improve the scientific approach and requirements through modeling scientific results grouping and assessing the main sources of errors reported by real-time simulations.
– Develop appropriate orbital models evaluate the requirements for the propulsion system to serve the station at a stable Lagrange point.
– Further improvement of the technological map necessary to make GO-LoW feasible in the next 10–20 years.
GO-LoW represents a revolutionary new paradigm for space missions. Achieves reliability through mass redundancy rather than exhaustive testing. You can develop and grow with new technologies rather than being locked into a fixed point of hardware and software development.
Finally, promise open a new spectral window into the universe where unexpected discoveries are sure to await.